Introduction to Internet Addressing
1. Introduction to Internet Addressing
- Simple Definition:
- Every device connected to the Internet has a unique address called an IP address, which allows it to communicate with other devices.
- इंटरनेट से जुड़े प्रत्येक उपकरण का एक विशिष्ट पता होता है जिसे आईपी पता कहा जाता है, जो उसे अन्य उपकरणों के साथ संचार करने की अनुमति देता है।
- Just like how every house has a unique address so the mailman knows where to deliver letters, every computer and device on the Internet has an IP address so data can be sent to the right place.
- जिस प्रकार प्रत्येक घर का एक विशिष्ट पता होता है ताकि डाकिया को पता रहे कि उसे पत्र कहां पहुंचाना है, उसी प्रकार इंटरनेट पर प्रत्येक कंप्यूटर और डिवाइस का एक आईपी पता होता है ताकि डेटा सही स्थान पर भेजा जा सके।
2. What is an IP Address?
- Simple Explanation:
- An IP address is a series of numbers that uniquely identifies a device on the Internet.
- Example of an IP Address:
192.168.1.1 - Analogy:
- Think of an IP address as a home address. Just like a house address tells the postman where to deliver a letter, an IP address tells the Internet where to send data.
3. Types of IP Addresses
- IPv4:
- Explanation:
- IPv4 is the most common version of IP addresses, made up of four sets of numbers separated by periods (e.g.,
192.168.0.1).
- IPv4 is the most common version of IP addresses, made up of four sets of numbers separated by periods (e.g.,
- IPv6:
- Explanation:
- IPv6 is a newer version that uses longer addresses with letters and numbers (e.g.,
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334), allowing for more unique addresses.
4. What is a Domain Name?
- Simple Explanation:
- A domain name is a user-friendly version of an IP address. Instead of typing a long string of numbers, we use domain names to visit websites.
- डोमेन नाम IP पते का एक उपयोगकर्ता-अनुकूल संस्करण है। संख्याओं की एक लंबी स्ट्रिंग टाइप करने के बजाय, हम वेबसाइटों पर जाने के लिए डोमेन नाम का उपयोग करते हैं।
- Example of a Domain Name:
www.google.com - Analogy:
- Think of a domain name as a contact name in your phone. Instead of remembering someone’s phone number, you save it under their name. Similarly, instead of remembering an IP address, you use a domain name.
- डोमेन नाम को अपने फ़ोन में मौजूद कॉन्टैक्ट नाम की तरह समझें। किसी का फ़ोन नंबर याद रखने के बजाय, आप उसे उसके नाम के नीचे सेव करते हैं। इसी तरह, IP एड्रेस याद रखने के बजाय, आप डोमेन नाम का इस्तेमाल करते हैं।
5. How Does DNS Work?
- DNS (Domain Name System):
- Explanation:
- DNS is like the Internet’s phone book. It translates domain names into IP addresses so computers can understand them.
- DNS इंटरनेट की फ़ोन बुक की तरह है। यह डोमेन नामों को IP पतों में बदल देता है ताकि कंप्यूटर उन्हें समझ सकें।
- Analogy:
- Imagine you want to call a friend. You look up their name in your contact list, and your phone dials the number. DNS does the same for websites, converting the name into an IP address.
- कल्पना करें कि आप किसी मित्र को कॉल करना चाहते हैं। आप अपनी संपर्क सूची में उसका नाम देखते हैं, और आपका फ़ोन नंबर डायल करता है। DNS वेबसाइट के लिए भी यही करता है, नाम को IP पते में बदल देता है।
- Example:
- When you type
www.google.comin your browser, DNS translates it to Google’s IP address, and your computer connects to it.
- When you type
6. Summary
- Recap Key Points:
- Every device on the Internet has an IP address, like a home address for computers.
- Domain names are easy-to-remember addresses for websites, translated into IP addresses by DNS.
1. Introduction to URLs
- Simple Definition:
- A URL is like a web address that you type into your browser to visit a specific page on the Internet.
- यूआरएल एक वेब पता जैसा होता है जिसे आप इंटरनेट पर किसी विशिष्ट पृष्ठ पर जाने के लिए अपने ब्राउज़र में टाइप करते हैं।
- Analogy:
- Think of a URL as the address of a house. Just as a house has a unique address that tells you where it is located, every page on the Internet has a unique URL that tells your web browser where to find it.
- URL को घर के पते के रूप में समझें। जिस तरह एक घर का एक अनूठा पता होता है जो आपको बताता है कि वह कहाँ स्थित है, उसी तरह इंटरनेट पर हर पेज का एक अनूठा URL होता है जो आपके वेब ब्राउज़र को बताता है कि उसे कहाँ खोजना है।
2. Parts of a URL
- Explain the Structure:
- A URL is made up of several parts, each serving a specific purpose. Let’s break it down using an example URL:
https://www.example.com/path/page.html.
- A URL is made up of several parts, each serving a specific purpose. Let’s break it down using an example URL:
Protocol:
- What It Is:
- The protocol is the first part of the URL and tells the browser how to communicate with the website’s server.
- प्रोटोकॉल URL का पहला भाग है और यह ब्राउज़र को बताता है कि वेबसाइट के सर्वर से कैसे संवाद करना है।
- Example:
https://orhttp://
- Analogy:
- The protocol is like the method of transportation you use to get to the address, such as driving a car or riding a bike.
- प्रोटोकॉल उस परिवहन पद्धति के समान है जिसका उपयोग आप पते पर पहुंचने के लिए करते हैं, जैसे कार चलाना या बाइक चलाना।
- Explanation:
https://is the secure version ofhttp://, meaning it encrypts the data sent between your browser and the website.
- What It Is:
Domain Name:
- What It Is:
- The domain name is the main part of the URL, which tells you the name of the website.
- डोमेन नाम URL का मुख्य भाग है, जो आपको वेबसाइट का नाम बताता है।
- Example:
www.example.com
- Analogy:
- The domain name is like the name of the building or house you are visiting.
- Explanation:
- This is the address of the website’s “home,” where you can find the main content.
- What It Is:
Path:
- What It Is:
- The path points to a specific page or folder within the website.
- Example:
/path/page.html
- Analogy:
- The path is like the room or specific area in the house you are visiting.
- Explanation:
- The path tells your browser which specific page to load on the website.
- What It Is:
File Name (Optional):
- What It Is:
- The file name indicates a specific file, such as a webpage or image, within the path.
- Example:
page.html
- Analogy:
- The file name is like the name of a document or file within the room you are visiting.
- Explanation:
- This is the exact page or file your browser will display.
Query Parameters (Optional):
- What It Is:
- Query parameters are extra information added to the URL to specify details like search terms.
- क्वेरी पैरामीटर अतिरिक्त जानकारी होती है जो खोज शब्दों जैसे विवरण निर्दिष्ट करने के लिए URL में जोड़ी जाती है।
- Example:
?search=books
- Analogy:
- Query parameters are like instructions for the search inside the building, such as asking for a specific book or document.
- क्वेरी पैरामीटर भवन के अंदर खोज के लिए निर्देशों की तरह होते हैं, जैसे किसी विशिष्ट पुस्तक या दस्तावेज़ के बारे में पूछना।
3. Practical Demonstration
Show How to Use a URL:
- Open a web browser and type a simple URL like
https://www.google.cominto the address bar. - Explain how the browser reads the URL and takes you to the website.
- Open a web browser and type a simple URL like
Breaking Down a URL:
- Take a more complex URL like
https://www.example.com/products/books.html?search=fictionand explain each part: - Protocol:
https:// - Domain Name:
www.example.com - Path:
/products/books.html - Query Parameters:
?search=fiction
ISP and Role of ISP
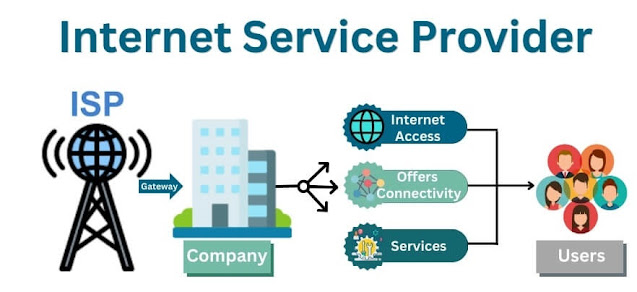
1. What is an ISP?
- Simple Definition:
- An ISP, or Internet Service Provider, is a company that provides you with access to the Internet. It’s like a utility company, but instead of providing water or electricity, it provides the Internet.
- ISP या इंटरनेट सेवा प्रदाता एक ऐसी कंपनी है जो आपको इंटरनेट तक पहुँच प्रदान करती है। यह एक उपयोगिता कंपनी की तरह है, लेकिन पानी या बिजली प्रदान करने के बजाय, यह इंटरनेट प्रदान करती है।
- Analogy:
- Think of an ISP as a bridge that connects your home to the Internet. Without an ISP, you wouldn’t be able to access websites, watch videos, or send emails.
- ISP को एक पुल के रूप में सोचें जो आपके घर को इंटरनेट से जोड़ता है। बिना ISP के, आप वेबसाइट एक्सेस नहीं कर पाएंगे, वीडियो नहीं देख पाएंगे या ईमेल नहीं भेज पाएंगे।
2. Role of an ISP
- Access to the Internet:
- The main job of an ISP is to connect you to the Internet. When you sign up with an ISP, they give you the tools and service needed to go online.
- ISP का मुख्य काम आपको इंटरनेट से जोड़ना है। जब आप किसी ISP के साथ साइन अप करते हैं, तो वे आपको ऑनलाइन होने के लिए ज़रूरी उपकरण और सेवा देते हैं।
- Provide Necessary Equipment:
- ISPs often provide the equipment needed to connect to the Internet, like a modem or a router.
- आईएसपी अक्सर इंटरनेट से कनेक्ट करने के लिए आवश्यक उपकरण, जैसे मॉडेम या राउटर, उपलब्ध कराते हैं।
- Analogy:
- It’s like getting a water meter from the water company so that water can flow into your home. The modem and router let the Internet flow into your home.
- यह पानी की कंपनी से पानी का मीटर लेने जैसा है ताकि पानी आपके घर में आ सके। मॉडेम और राउटर आपके घर में इंटरनेट को प्रवाहित करते हैं।
- Customer Support:
- ISPs offer support to help you with any issues related to your Internet connection, like if your connection is slow or if you can’t get online.
- आईएसपी आपके इंटरनेट कनेक्शन से संबंधित किसी भी समस्या में आपकी सहायता करने के लिए समर्थन प्रदान करते हैं, जैसे कि यदि आपका कनेक्शन धीमा है या आप ऑनलाइन नहीं हो पा रहे हैं।
- Provide Additional Services:
- Many ISPs also offer extra services like email accounts, web hosting, or even TV and phone services.
- कई आईएसपी अतिरिक्त सेवाएं भी प्रदान करते हैं, जैसे ईमेल खाते, वेब होस्टिंग या यहां तक कि टीवी और फोन सेवाएं भी।
3. How Does an ISP Work?
- Connecting to the Internet:
- When you want to go online, your device sends a request to the ISP, which then connects you to the Internet. This connection happens through various technologies like DSL, cable, fiber-optic, or satellite.
- जब आप ऑनलाइन जाना चाहते हैं, तो आपका डिवाइस ISP को अनुरोध भेजता है, जो फिर आपको इंटरनेट से जोड़ता है। यह कनेक्शन DSL, केबल, फाइबर-ऑप्टिक या सैटेलाइट जैसी विभिन्न तकनीकों के माध्यम से होता है।
- Example:
- Imagine you want to visit a website. Your device sends the request to your ISP, which then finds the website on the Internet and sends it back to your device so you can see it.
- कल्पना करें कि आप किसी वेबसाइट पर जाना चाहते हैं। आपका डिवाइस आपके ISP को अनुरोध भेजता है, जो फिर इंटरनेट पर वेबसाइट ढूंढता है और उसे आपके डिवाइस पर वापस भेजता है ताकि आप उसे देख सकें।
.jpeg)




.jpeg)

Good 👍 sir
ReplyDeleteGood👍
ReplyDeletethank you sir very easy topic
ReplyDelete1 c
ReplyDelete2.c
ReplyDelete